
Pharmaceutical waste encompasses various Types of Pharmaceuticals Waste and Disposal Procedure including expired or unused medications, contaminated materials from pharmaceutical manufacturing processes, and even packaging materials.
Here are some common Types of Pharmaceuticals Waste and Disposal Procedure and general disposal procedures.
INTRODUCTION
The destruction of wastage materials is particularly important. A potential source of contamination shall be eliminated through comprehensive program of disposal. The garbage shall be destructed or removed frequently and thoroughly in accordance with the written program approved by Quality Control Department. Garbage consists of different waste materials, waste materials shall not be allowed to accumulate and it shall be collected in suitable receptacles for removal to collection points out side the buildings and disposed of safely and in a sanitary manner at regular and frequent intervals.
The rough things must be thrown in the respective garbage boxes that are properly labeled showing the status VS identifications. All the dustbins must be emptied carefully especially while cleaning the chemical dustbins near the more sophisticated instruments. There shall be effluent control system
The sweeper concerned with the Q.C lab must be trained properly garbage is of following type.
Types of Pharmaceutical Waste
- Expired or Unused Medications:
- Papers
- Glass Apparatus
- Toxic and non-toxic chemicals
- Reagent & solution bottles
- Chemical bottles
- Microbial waste
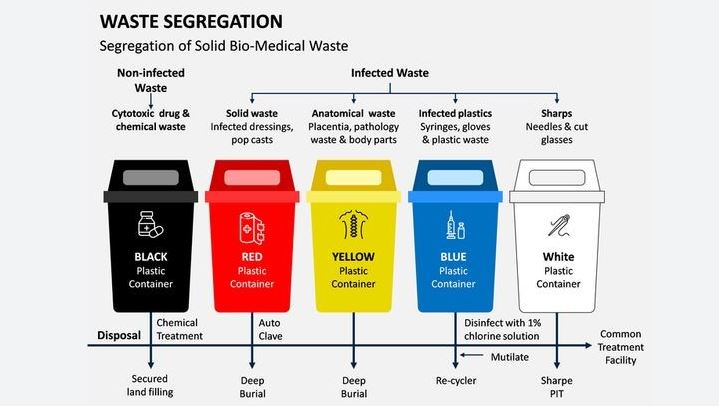
RESPONSIBILITY
Quality Control Lab. Assistant and sanitary inspector are responsible for the disposal of waste materials from quality control department.
DISPOSAL PROCEDURE OF WASTE MATERIALS
Expired or Unused Medications:
- Collect expired or unused medications from households, healthcare facilities, and pharmacies.
- Segregate them based on their properties (e.g., solid, liquid, controlled substances).
- Dispose of non-controlled substances:
- Incineration: Some pharmacies and healthcare facilities have agreements with waste management companies that handle pharmaceutical waste incineration.
- Landfill disposal: Follow local regulations for landfill disposal of non-hazardous pharmaceutical waste.
- Controlled substances:
- Reverse distribution: Return controlled substances to manufacturers or authorized reverse distributors for proper disposal.
- DEA-compliant disposal: Use DEA-registered reverse distributors or follow DEA guidelines for controlled substance disposal, which may involve incineration or chemical destruction.
Disposal of papers:-
Frequency: Twice a day
Responsible person sweeper
The garbage consists of daily wastage papers line butter papers, tissue papers must be thrown into the dustbin that labeled for waste papers.
Disposal of Glass Apparatus:-
Frequency: Once Daily
Responsible person sweeper
The glass wares e.g. Pippets, Cylinders, Test tubes, Beaners, flasks etc. if broken must be thrown in a dustbin that is properly labelled for this type of waste materials.
The broken glassware then must be destroyed in a glassware store in the presence of a responsible active member after the permission of the department head.
Disposal of toxic and non toxic chemicals
Responsible persons
The waste materials consists of toxic chemicals must be carefully disposed of in a tightly closed dustbin as soon as possible.
The non-toxic waste chemicals must be thrown in a specific dustbin and then are disposed of by plenty of water.
Care must be taken while cleaning the chemicals dust bins near the more sophisticated instruments the record of the materials i.e. chemicals must be maintained properly.
Disposal of reagent and solution bottles:-
The amber caloured reagent bottles and transported solution bottles if broken must be thrown into a dustbin which is labelled for glass apparatus wastage the spare or emptied glass bottles are kept or put in a specified labelled shelf. Then these broken and emptied glass bottles are destroyed in a broken glass store in the presence of a responsible active member after the permission of head of Q.C. department.
Disposal of chemical bottles:-
Frequency Responsible person: Q.C. Assistant:-
The empty plastic chemicals bottles are collected in a fixed properly labelled shelf and then send to the stove for destruction or removal.
Disposal of Microbial waste:-
Frequency: Once daily
Responsible person: sweeper
The microbial waste in petridishes and test tubes must be disposed of carefully according to the nature of microbial toxicity and pathogenically.
Destruction of Media
The disposable petridishes and strips used in microbial test are discarded.
The microbial waste consists of specimens, cultures, and others contaminated materials and equipment like petridishes, test tubes used to test such material must be made non-infections before being discarded or cleaned for reuse. All material is sterilized to ensure the destruction or removal of all living forms.
The microbial waste is destroyed as soon as possible. Laboratory waste which include reusable articles may be decontaminated using disinfectants or by physical means.
Sometime the waste microbial material is burned to incinerate infected materials, in such case the waste is placed in metal container and is placed in a center of waste fire the temperature is high enough to kill all organism and non can escape in smoke or air draughts.
Cleaning of Dustbins
Frequency: Once daily
Responsible persons: sweeper
After destroying the garbage or waste materials the sweeper wash all the dustbins with detergents and disinfectants out of the Q.C. department of area. The dustbin are then dried and kept at proper of fixed place for reuse.
Detergents and disinfectant solutions:-
Types of Pharmaceuticals Waste and Disposal Procedure
For cleaning and disinfection following detergents and solutions are used.
a. Detergents (Vim or Surf)
b. Phenyl 5% (Finis)
c. Chloroxylenol 2%
ARCHIVING
The original SOP’s is to be archived in such a way that they are protected from unauthorized use. It is stored on computer in which a priority system is established that allows access only to members of the Quality Control Department (including persons authorized by them). Storage of SOP’s in the computer network is permitted under strict adherence to the rights of access and the original print of Types of Pharmaceuticals Waste and Disposal Procedure will be store for 5 years in Quality Control Manager office.
TRAINING
Periodical Training Types of Pharmaceuticals Waste and Disposal Procedure
The staff, that is responsible for performance of this operating instruction, has to be taught demonstrably about the content of this SOP together with the GMP training once in a year.
Training for New Employees:
Before starting with the job, the employee has to be taught demonstrably about the content of this SOP.


An interesting discussion is definitely worth comment.
I do think that you ought to write more about this subject
matter, it might not be a taboo matter but usually
people do not speak about such issues. To the next! All the best!!