Cleaning Validation SOP is for collecting samples for cleaning sample from equipment and machines for Cleaning validation SOP.
Cleaning Validation SOP Importance:
Cleaning Validation SOP have it own importance for the maintenance cleaning of equipment and machines, which provide us Quality products.
1. PURPOSE
Main objective of the Cleaning Validation SOP is as following:
1.1 Describe a procedure for collecting samples for cleaning validation from different equipments / machines used in manufacturing to identify the traces of previous product that may contaminate the batch of subsequent product.
1.2 Eliminate chances of contamination or cross contamination of subsequent product manufactured.
1.3 Validate the procedures used for cleaning of equipments / machines used in manufacturing and packaging of products.
2. SCOPE
This procedure is applicable for validation of all cleaning procedures used for equipments/machines (present in Baariq Pharma premises) which are in direct contact with product.
3. RESPONSIBILITY
3.1 Production sections are responsible to performs cleaning of equipments as per Cleaning Validation SOP and coordinate Q.A Deptt. in cleaning validation activities.
3.2 Quality Assurance Officer is responsible to prepare the Cleaning Validation Protocol with the consultation of Cleaning Validation Team (comprising of Section Head, Q.C Manager & Quality Assurance Manager).
3.3 Q.A Manager approves the Cleaning Validation Protocol.
3.4 Production Pharmacist & Q.A Officer monitors the whole activity of Cleaning Validation and Q.A Officer performs sampling of cleaning validation.
3.5 Q.A Manager is responsible for ensuring the activity.
3.6 Quality Control Manager is responsible to develop and validate analytical method for cleaning validation samples.
3.7 Quality Control Analysts are responsible for testing of cleaning validation samples and respective documentation.
3.8 Q.A Officer is responsible to prepare cleaning validation report.
3.9 Cleaning Validation Report is approved by Q.A Manager.
4. MATERIAL & EQUIPMENT
Materials required for sampling,
4.1 Cotton Swabs
4.2 Purified Water
4.3 100ml Stoppard volumetric flask
4.4 1L Plastic Jug
4.5 Measuring Tape
4.6 10x10cm S.S. template
4.7 Cleaning validation label
5. PROCEDURE
5.1 Selection of Products and Equipments for the conduction of Cleaning Validation is carried out as per worst case scenario.
5.2 Worst Case Product is selected on the basis of following criteria
5.2.1 Difficult to Clean
5.2.2 Low Water Solubility / Insoluble in Water and Toxic
5.3 Select one product from each dosage according to above cited criteria.
5.4 Dedicated equipments for one product are exempted from Cleaning Validation.
5.5 Cleaning validation for each worst case product is conducted on Three (3) consecutive batches of that product for each machine/equipment.
5.6 Production Pharmacist prepares the “Schedule for Cleaning Validation” upto the column of equipment # (remaining columns are filled during Cleaning Validation study by QA) as per products and equipments selected for cleaning validation in Cleaning Validation Policy.
5.7 Schedule is reviewed by Production Manager, Q.C Manager.
5.8 This schedule is finally approved by Q.A Manager.
5.9 A copy of this schedule is kept by production section while original is sent to Q.A Deptt.
5.10 Worst case(s) selection is being done as per Cleaning Validation Policy and any new product require cleaning validation will be evaluated on this policy which is reviewed on yearly basis during Annual Product Reviews.
5.11 From selected product (having more than one API) that active is selected as worst case, which is least soluble in water and more toxic. In collecting the toxicity data, preference is given to data with similar mode of administration as that of product.
5.12 Cleaning Validation Protocol :
5.12.1 Cleaning Validation Protocol is prepared for each equipment, selected for cleaning validation by Q.A Officer with the consultation of Cleaning Validation Team.
5.12.2 Cleaning Validation Protocol is approved by Q.A Manager which includes
a. Study design
b. Document to be checked
c. List of documents / record forms to be attached
d. List of equipments to be used
e. List of tests to be performed along with their acceptance criteria
f. Carry over limit calculations
g. Sampling Plan along with test to be performed and responsibility
h. Calculation of residual contamination
i. Deviation report
j. Any change(s) suggested
k. Summary of Cleaning Validation
5.12.3 Protocol Numbers for Cleaning Validation Protocol (CVP) and Report Numbers for Cleaning Validation Report (CVR) are assigned by Q.A Officer from Cleaning Validation Log Book at the time of approval of protocol.
5.12.4 To allot Protocol No. and Report No., a uniform numbering System is followed as CVX/PPP/000
CVX = Type of Cleaning Validation (Protocol or Report) e.g. CVP or CVR.
PPP = Product Code (product selected for cleaning validation)
000 = Serial Number.
Example:
Protocol No. and Report No. for Cleaning Validation of equipment used for Ibuprofen suspension is as follow,
Protocol No. = CVP/IB/001, Report No. = CVR/IB/001
5.12.5 Serial Number of Report No. is same as its serial # in Protocol No. Serial # is allotted from the Cleaning Validation Log Book and goes on increasing with new protocol prepared for each equipment.
5.12.6 Purpose of Cleaning validation, scope and responsibilities is described on Page 1 of Cleaning Validation Protocol.
5.12.7 Study design is described on page 2 of Cleaning Validation Protocol, include
a. Equipment Description
b. Selection of Critical Sampling Locations & Sampling Methods
c. Selection of Worst Case Product / Active
d. Carry over limit calculation
e. Selection of Analytical Method
f. Planning & Execution
g. Monitoring & maintenance
5.12.8 All the Cleaning and Sampling/ Testing documents required and List of documents/ records forms to be attached & equipments to be used are described on page 3 of Cleaning Validation Protocol.
5.12.9 List of all the tests to be performed along with their procedure and acceptance criteria are described on page 4 of Cleaning Validation Protocol.
5.12.10 Carry over limit calculation is described on page 5 of Cleaning Validation Protocol. This page can be repeated if carry over limit needs to be calculated for more than one APIs.
5.12.11 A sampling plan which includes equipment, sampling method, sampling point, sampling procedure, sample quantity, sampling container, sampling to be performed by, tests to be performed along with procedure and responsibility are described on page 6 of Cleaning Validation Protocol.
5.12.12 Calculation of residual contamination format is described on page 7 of Cleaning Validation Protocol.
5.12.13 Deviation report format is described on page 8 of Cleaning Validation Protocol.
5.12.14 Format for any change(s) suggested during Cleaning Validation study is described on page 9 of Cleaning Validation Protocol.
5.12.15 Format for Summary of Cleaning Validation study is described on page 10 of Cleaning Validation Protocol.
5.13 Production Pharmacist and Q.A Officer ensures that the cleaning of the equipment is carried out as per approved SOP and by the trained worker(s).
5.14 TYPES OF SAMPLING :
Cleaning validation samples are collected by following two methods,
e.g., Direct Surface Sampling (Swab Method) and Indirect Sampling (use of rinse solutions)
5.14.1 DIRECT SURFACE SAMPLING (SWAB METHOD) :
a. Areas which are hardest to clean and their rinse sampling cannot be performed, are evaluated by direct sampling method (i.e. Rotary Machines, Blister Machine etc.) after cleaning.
b. Sampling is done with cotton swabs soaked in Purified water.
c. Before sampling Q.A Officer visually inspects the equipment / machine for Cleanliness, if cleaning is satisfactory (i.e. no visible residue exists) then he / she takes the sample for cleaning validation according to approved sampling points in Protocol.
d. During sampling cotton swab soaked with purified water is rubbed on selected area of the equipment / machine which is in direct contact with product, after swabbing put the swab back to labelled swab tube.

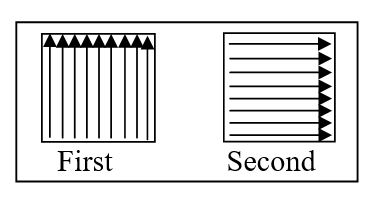
e. Cotton swab is rubbed on the selected area from one side to another as shown in below diagram of 10×10 cm template ensuring that contaminated swab or part of swab not used for next rubbing. New swab is used for sampling
of further area remaining for sampling. In the last a swab is rubbed in the direction “as shown in Second” and shifted back to labelled swab tube.
f. Equipment parts such as punches, chutes etc. as in case of compression machine etc. are swabbed completely.
g. More than one swab can be used for sampling of machine / equipment and composite sample is prepared for testing.
h. Sampling Area:
For sampling 10×10 cm S.S. template is used. For area where 10×10 cm S.S. template cannot be used (for example curved areas) or where the total product contact surface area is less than 10×10 cm, a measuring tape is used for sampling area measurements.
i. Samples from different locations / spots are collected and analyzed separately.
j. After sampling, sample is sent to Q.C for analysis of any traces of previous product API(s).
5.14.2 INDIRECT SAMPLING (USE OF RINSE SOLUTIONS) :
a. Rinse sampling method allows sampling of large surface area which can easily be washed with plenty of water (like Bin Blenders, Film coating machine tablet pan etc).
b. Before sampling Q.A Officer visually inspects the equipment / machine for Cleanliness, if cleaning is satisfactory (i.e. no visible residue exists) then he / she manages to take the sample for cleaning validation.
c. Equipment / machine is finally rinsed with definite quantity of Purified water & sampled as per protocol.
d. Quality Assurance Officer collects about 100 ml sample (in cleaned Stoppard volumetric flask) from this rinse and sends to Quality Control Department for its testing.
5.15 Quality Control Deptt. informs Production Section about the results of cleaning validation samples on Cleaning Validation test report.
5.16 Cleaning Validation Report :
5.16.1 Cleaning Validation Report is prepared by Q.A Officer which includes
a. Purpose, scope, responsibilities and General description of Cleaning validation and is described on Page 1 of Cleaning Validation Report.
b. All the Cleaning and Sampling/ Testing documents checked and List of documents/ records forms attached & equipments used with models, codes and re-calibration dates are reported on page 2 of Cleaning Validation Report.
c. Cleaning verifications and conductivity measurements (in case of rinse samples) are reported on page 3 of Cleaning Validation Report.
d. Carry over limit calculation is reported on page 4 of Cleaning Validation Report. This page can be repeated if carry over limit needs to be calculated for more than one APIs.
e. Deviation report (if any) with justification of acceptance along with impact on operation is described on page 5 of Cleaning Validation Report.
f. Any change(s) suggested during Cleaning Validation study along with reason for change is described on page 6 of Cleaning Validation Report.
g. After cleaning validation completion, final summary of cleaning validation study is described on page 7 of Cleaning Validation Report by Officer QA which is reviewed by Production Manager, Q.C Manager and Approved by Q.A Manager.
5.16.2 This report is retained by Q.A. Deptt.
5.16.3 Cleaning Validation team reviews the need for repeat cleaning validation whenever there is change in,
a. Cleaning Procedure
b. Equipment (modified/replaced)
5.17 Sampling for this equipment for cleaning validation is carried out again for next 2 consecutive batches (total 3) of same product is manufactured on this equipment.
5.18 During cleaning validation machine is not hold till results.
5.19 In case of cleaning validation sample failure in testing or unsatisfactory results, Q.A Officer and Production Pharmacist investigate the root cause of failure in testing or unsatisfactory results and take the necessary actions which may result in,
• Change in cleaning procedure • Change in operator etc.
5.20 Periodic cleaning validation is carried out after every five years for equipment chain of the selected equipments.
6. REPORTING
6.1 Cleaning validation SOP. Log Book
6.2 Schedule for Cleaning validation SOP.
6.3 Cleaning Validation Protocol
6.4 Cleaning Validation Report
6.5 Cleaning Validation test report as described in Cleaning Validation SOP
7. REFERENCE DOCUMENTS
7.1 Analytical procedures for Cleaning Validation Samples
7.2 WHO guideline for Cleaning Validation.
7.3 Cleaning Validation Guidelines, issued on 2000-05-01 (Health Product and Food Branch inspectorate Canada)
7.4 Cleaning Validation SOP (Pharmaceutical Quality Group Monograph No. 10, The Institute of Quality
Assurance United Kingdom).
7.5 The Registry of Toxic Effect of Chemical Substances (Web Site)

